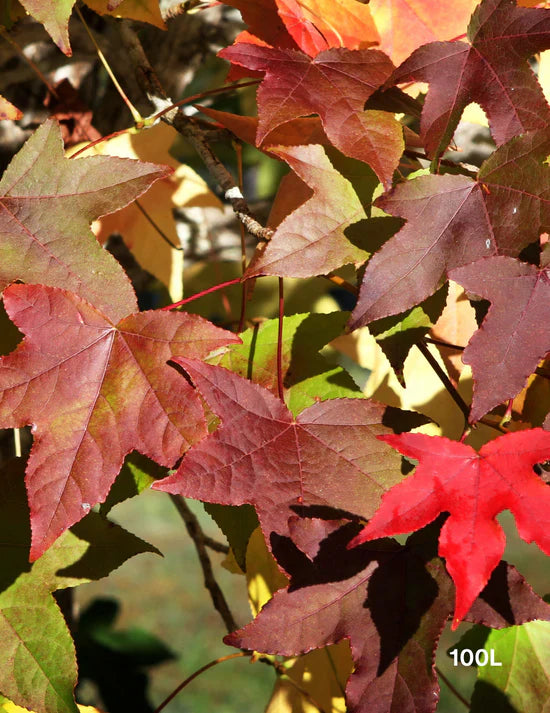
Soil is the lifeblood of any garden, and understanding the different types can be crucial to ensuring that your trees thrive. As spring approaches and gardeners prepare to plant, knowing how various soil types affect tree health and growth becomes more important. This guide will explore how different soil types interact with trees like Acer Rubrum, Liquidambar Styraciflua, and Acer campestre. By the end of this article, you'll be equipped with the knowledge to make informed decisions for your spring garden preparation.
The Importance of Soil in Tree Growth
Soil is more than just dirt; it’s a complex system that provides essential nutrients, water, and support to your trees. The soil type in your garden can significantly impact your trees' health, growth rate, and overall vitality. Understanding soil types allows you to tailor your tree selection and care practices to ensure your garden flourishes.
Common Soil Types and Their Characteristics
1. Sandy Soil
- Texture: Gritty and coarse, with large particles that create significant space between them.
- Drainage: Excellent drainage, but it can lead to water and nutrient loss.
- Impact on Trees: Trees like Acer campestre (Field Maple) can struggle in sandy soil due to poor nutrient retention. However, proper mulching and regular fertilization can improve soil conditions to support the tree's growth.
2. Clay Soil
- Texture: Fine and sticky when wet, forming clumps that can be challenging to work with.
- Drainage: Poor drainage, which can lead to waterlogging and root rot.
- Impact on Trees: Liquidambar Styraciflua (Sweet Gum) is well-suited for clay soils due to its robust root system tolerating less-than-ideal drainage. However, amending the soil with organic matter can improve its structure and reduce the risk of waterlogging.
3. Loamy Soil
- Texture: Loamy soil, a balanced mix of sand, silt, and clay, is often considered ideal for gardening.
- Drainage: Good drainage while retaining moisture and nutrients effectively.
- Impact on Trees: Acer Rubrum (Red Maple) thrives in loamy soil, which provides the perfect balance of moisture and nutrients for its growth. Loamy soil’s excellent properties make it ideal for most tree species, supporting healthy root development and vigorous growth.
4. Silty Soil
- Texture: Smooth and slippery, with medium-sized particles that retain moisture well.
- Drainage: Holds moisture better than sandy soil but can become compacted easily.
- Impact on Trees: Acer campestre can benefit from silty soil due to its moisture-retention capabilities. However, incorporating organic matter and ensuring proper drainage are essential to avoid compaction.
5. Peaty Soil
- Texture: Dark, spongy, and rich in organic material, with a high acid content.
- Drainage: Excellent moisture retention but can become waterlogged if not managed properly.
- Impact on Trees: Peaty soil can benefit acid-loving trees. However, it may require liming to reduce acidity for trees like Liquidambar Styraciflua, which prefers slightly acidic to neutral soil conditions.
How Soil Affects Tree Health and Growth
1. Nutrient Availability
- Sandy Soil: Nutrients can leach away quickly due to poor retention, requiring regular fertilization.
- Clay Soil: Nutrient-rich but can become compacted, limiting root access to nutrients.
- Loamy Soil: Ideal nutrient balance, promoting strong and healthy tree growth.
- Silty Soil: Holds nutrients well but may require soil amendments to improve structure.
- Peaty Soil: High in organic material but may need pH adjustment for certain trees.
2. Water Retention and Drainage
- Sandy Soil: Excellent drainage but prone to drought stress.
- Clay Soil: Poor drainage, risking waterlogging and root diseases.
- Loamy Soil: Balanced water retention, supporting healthy root systems.
- Silty Soil: Good water retention but vulnerable to compaction.
- Peaty Soil: Retains moisture well but may need careful management to avoid waterlogging.
3. Root Growth
- Sandy Soil: Encourages deep root growth due to easy penetration but can cause drought stress.
- Clay Soil: Restricts root growth unless amended to improve texture.
- Loamy Soil: Promotes extensive and healthy root systems, ideal for most trees.
- Silty Soil: Supports moderate root growth but requires proper aeration.
- Peaty Soil: Favors shallow root systems with a risk of waterlogged roots.
Choosing the Right Trees for Your Soil Type
Understanding your soil type is key to selecting the right trees for your garden. Each tree species has specific requirements that must be met for optimal growth. Here’s how the mentioned trees adapt to different soils:
- Acer Rubrum: Prefers loamy, well-drained soils but can tolerate various soil types if adequately cared for. This versatility makes it a favorite for diverse landscapes.
- Liquidambar Styraciflua: Thrives in clay soils where its roots can anchor firmly despite poor drainage. Its tolerance for slightly acidic conditions also makes it adaptable to peaty soils.
- Acer campestre: While it prefers loamy or silty soils, it can grow in sandy soils with proper amendments, making it a versatile choice for challenging landscapes.
Tips for Improving Soil Conditions
1. Soil Testing
- Before planting, test your soil to determine its type and nutrient content.
- Use soil test kits or consult a local agricultural extension service for accurate results.
2. Soil Amendments
- Organic Matter: Incorporate compost or manure to improve soil structure, nutrient content, and moisture retention.
- Mulching: Apply mulch to regulate soil temperature, retain moisture, and prevent compaction.
- Lime or Sulfur: Depending on your tree species' needs, adjust pH levels with lime (to reduce acidity) or sulfur (to increase acidity).
3. Proper Watering Practices
- Tailor your watering schedule to your soil type, ensuring that trees receive adequate moisture without risking waterlogging.
- Consider installing a drip irrigation system for precise watering control.
4. Aeration
Regularly aerate compacted soils, particularly clay, and silty types, to enhance root growth and water penetration.FAQs
1. What is the best soil type for trees?
- Loamy soil is generally considered the best for tree growth due to its balanced texture, nutrient retention, and drainage.
2. Can trees grow in sandy soil?
- Trees like Acer campestre can grow in sandy soil, but they require regular fertilization and mulching to retain moisture and nutrients.
3. How can I improve clay soil for tree planting?
- Incorporating organic matter, such as compost, can significantly improve clay soil by enhancing its structure and drainage.
Conclusion
Understanding different soil types and their impact on tree growth is vital for creating a thriving garden. By selecting the right trees for your soil type and making the necessary amendments, you can ensure your garden flourishes year-round. Whether planting the vibrant Acer Rubrum, the resilient Liquidambar Styraciflua, or the adaptable Acer campestre, the right soil preparation is the key to success.